How Does Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Work? Understanding the Science Behind HBOT
This is a subtitle for your new post

Introduction
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) is a groundbreaking medical treatment that utilizes pure oxygen at increased atmospheric pressure to promote healing and recovery. Originally developed for decompression sickness in divers, HBOT has since been recognized for its ability to enhance tissue repair, reduce inflammation, and improve neurological function.
But how exactly does HBOT work? What happens in the body when exposed to high-pressure oxygen, and why is it effective for conditions like wound healing, stroke recovery, and chronic inflammation? In this guide, we’ll break down the scientific mechanisms behind HBOT, explaining how oxygen therapy supports cellular repair, immune function, and vascular regeneration.
The Basics of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
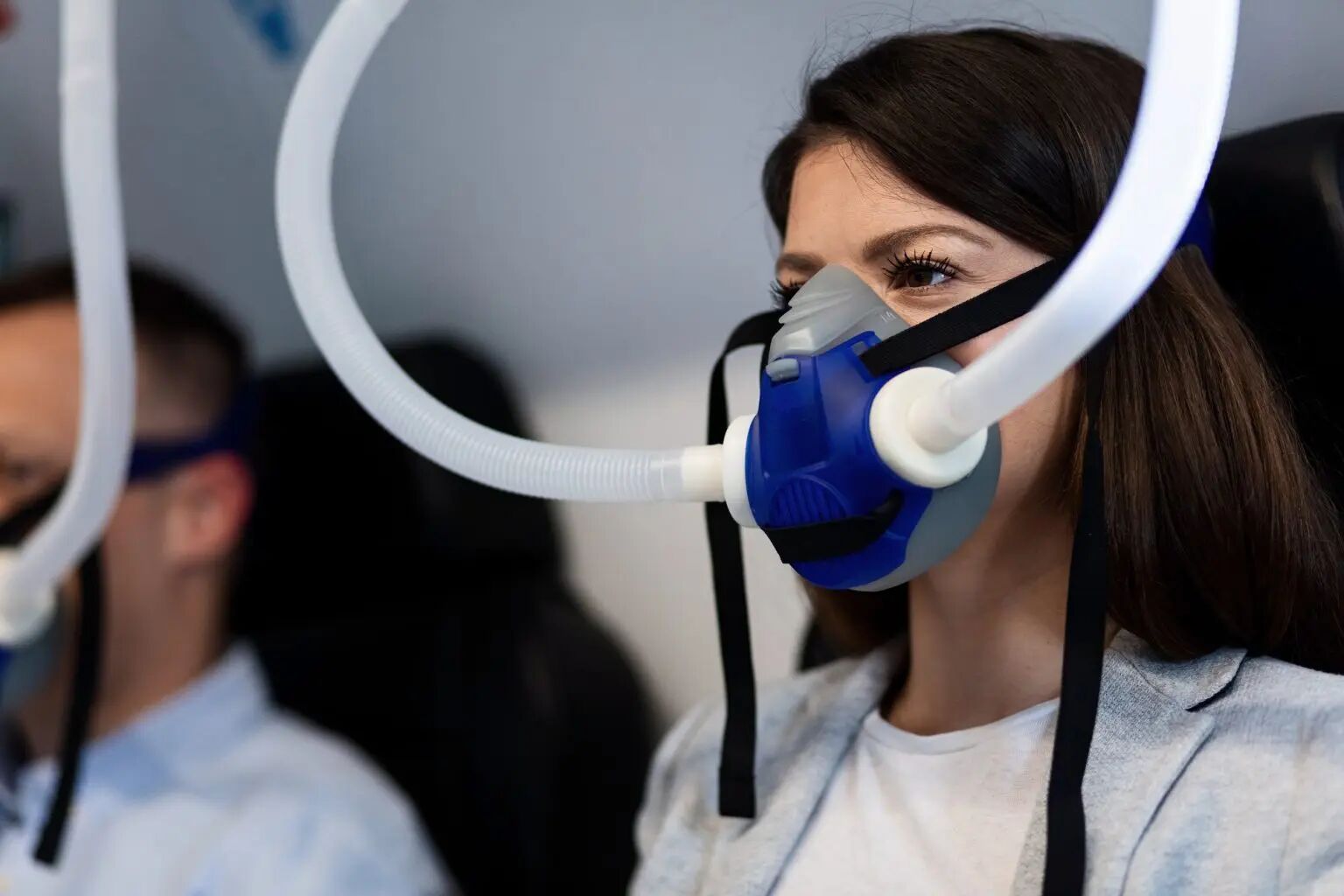
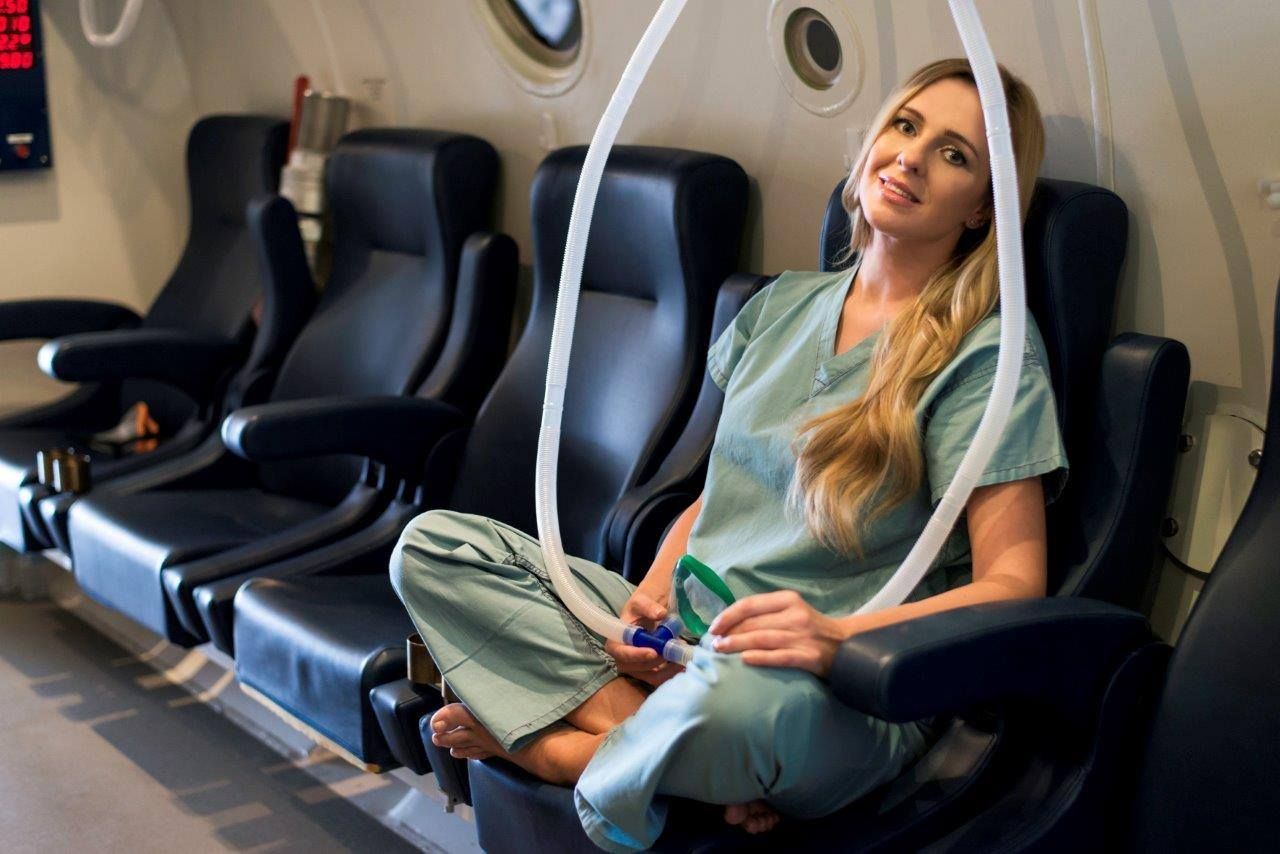
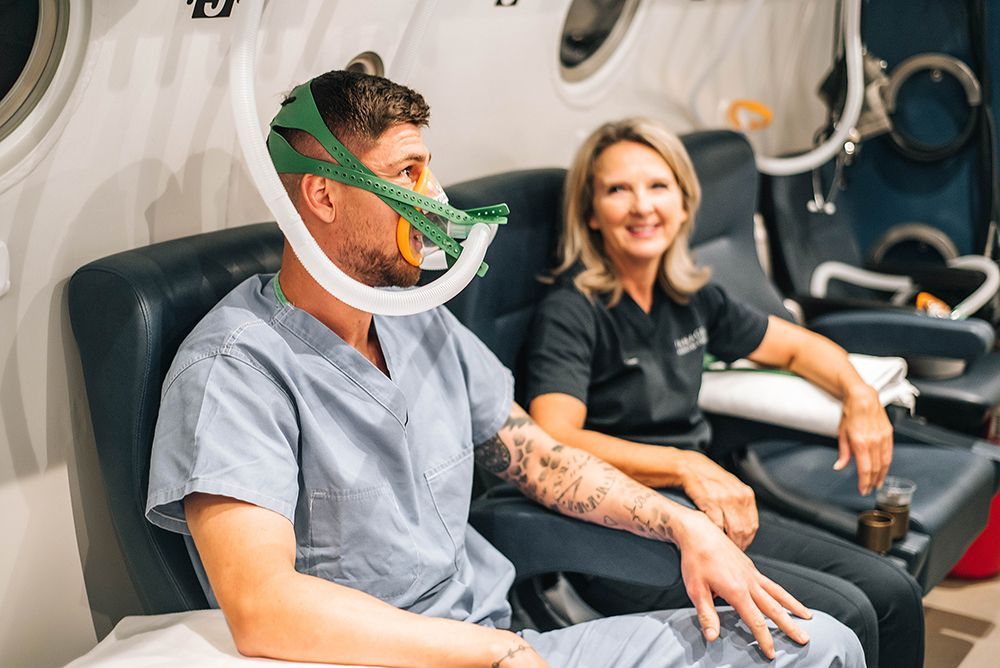
HBOT is a non-invasive therapy in which patients breathe 100% oxygen inside a hyperbaric chamber, typically at 1.5 to 3 times atmospheric pressure. This process enhances oxygen delivery throughout the body, even to areas with poor circulation or damage.
Hyperbaric Chambers: How They Work
There are two main types of hyperbaric chambers:
- Monoplace chambers – Single-person chambers that resemble a clear, tube-like capsule.
- Multiplace chambers – Larger chambers accommodating multiple patients, where oxygen is delivered via masks or hoods.
During a session (usually 60-90 minutes), the increased atmospheric pressure forces more oxygen into the bloodstream, plasma, and tissues, accelerating recovery.
The Science Behind HBOT: Oxygen, Pressure, and Healing
HBOT relies on two key scientific principles:
- Henry’s Law – The amount of gas (oxygen) dissolved in a liquid (blood plasma) increases with pressure. In an HBOT chamber, oxygen dissolves directly into plasma, reaching tissues beyond what red blood cells alone can supply.
- Boyle’s Law – As pressure increases, the volume of gas decreases. This helps reduce gas bubbles in the bloodstream (crucial for treating decompression sickness).
By increasing oxygen concentration at the cellular level, HBOT creates an environment that enhances tissue repair and fights infection.
Key Physiological Effects of HBOT
1. Enhanced Tissue Oxygenation
Under normal conditions, oxygen is transported by red blood cells. However, during HBOT, oxygen dissolves directly into plasma, allowing it to reach areas with low blood flow (ischemia), such as:
- Wounds & ulcers in diabetic patients
- Damaged brain tissue post-stroke or traumatic brain injury
- Inflamed tissues in autoimmune disorders
🔗 Study: A 2021 study in Advances in Wound Care found that HBOT significantly improves oxygen diffusion in chronic wounds, reducing healing time (Kranke et al., 2021).
2. Cellular Repair & Regeneration
Oxygen is essential for
cellular metabolism and ATP production (the energy source of cells). Increased oxygen levels:
✅
Boost mitochondrial function (energy production)
✅
Stimulate stem cell activation for faster healing
✅
Reduce oxidative stress and support anti-aging mechanisms
🔗 Study: Research in Cell Metabolism (2022) demonstrated that HBOT activates hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF-1α), which promote stem cell production (Efrati et al., 2022).
3. Angiogenesis (New Blood Vessel Formation)
One of HBOT’s most powerful effects is its ability to stimulate angiogenesis, the growth of new blood vessels. This process is crucial for:
- Healing damaged tissues after surgery
- Recovering from radiation-induced injuries
- Restoring blood flow in ischemic areas (e.g., post-stroke recovery)
🔗 Study: A 2020 study in Journal of Vascular Research confirmed that HBOT upregulates VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor), a key molecule in blood vessel formation (Thom et al., 2020).
4. Reduction in Inflammation & Oxidative Stress
Chronic inflammation is a major factor in conditions like
fibromyalgia, arthritis, and autoimmune diseases. HBOT helps by:
✅
Decreasing pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6)
✅
Increasing antioxidant enzyme activity (superoxide dismutase, catalase)
✅
Modulating immune response to prevent tissue damage
🔗 Study: A 2023 Frontiers in Immunology review found that HBOT significantly reduces inflammation markers in long COVID and chronic fatigue syndrome patients (Hadanny & Efrati, 2023).
5. Antimicrobial Effects & Immune Boosting
Oxygen plays a direct role in the body’s ability to fight infections. High oxygen concentrations:
- Kill anaerobic bacteria (e.g., those causing gangrene)
- Enhance white blood cell activity
- Promote collagen production for wound healing
🔗 Guidelines: The Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society (UHMS) recognizes HBOT as a first-line treatment for necrotizing infections and gas gangrene (www.uhms.org).
HBOT’s Role in Treating Various Conditions
HBOT is FDA-approved and widely studied for treating:
✅
Diabetic Foot Ulcers – Enhances wound healing and prevents amputations
✅
Neurological Disorders – Improves recovery in stroke and traumatic brain injury (TBI)
✅
Chronic Pain Syndromes – Helps in fibromyalgia, arthritis, and inflammatory diseases
✅
Radiation Damage – Restores tissues damaged by cancer treatments
🔗 Clinical Trial: A randomized controlled trial in PLOS One (2023) showed that long COVID patients treated with HBOT reported improved brain function and reduced fatigue compared to placebo (Zilberman-Itskovich et al., 2023).
Addressing Common Misconceptions About HBOT
🚫
Myth: HBOT is a “miracle cure” for any disease.
✅
Truth: While highly effective for many conditions, HBOT works best when
used alongside traditional medical treatments.
🚫
Myth: Too much oxygen is dangerous.
✅
Truth: HBOT is
carefully regulated; under proper supervision, the risk of oxygen toxicity is minimal.
The Future of Hyperbaric Medicine
Emerging research suggests HBOT may have potential applications in:
- Neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s)
- Aging and longevity medicine
- Enhancing sports recovery & cognitive performance
Ongoing clinical trials are further exploring its role in cancer recovery, PTSD treatment, and metabolic disorders.
Conclusion
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy is a scientifically backed, FDA-approved treatment that enhances healing, reduces inflammation, and improves neurological function. By increasing oxygen levels at the cellular level, HBOT offers hope for patients suffering from chronic wounds, neurological damage, and inflammatory conditions.
For those considering HBOT, consult a medical professional to determine whether this innovative therapy is right for you.
FAQs
1. How many HBOT sessions are needed to see results?
Most patients see benefits after
10-40 sessions, depending on their condition.
2. Can HBOT improve athletic performance?
Yes! HBOT is used by elite athletes to
speed up recovery and enhance endurance.
3. Is HBOT safe for people with heart conditions?
In most cases, yes, but always consult a doctor first.
4. What’s the difference between mild HBOT and high-pressure HBOT?
Mild HBOT (1.3 ATA) is often used for wellness, while medical HBOT (2.0-3.0 ATA) is for
serious conditions.
5. Are there risks of too much oxygen exposure?
Only if improperly administered. Under supervision, HBOT is
safe and effective.